The term HDR is an abbreviation for the phrase (high dynamic range), and it is a term that has been widely used recently in many fields, and one of these fields is the field of photography.
Photographers use this term a lot, and learning new photography terms can be overwhelming, but don't worry – the idea of HDR is much simpler than you think.
What is HDR (in general)
HDR stands for high dynamic range and is used to describe anything that can handle a wider range of inputs or outputs than a standard device of the same type. It is commonly used when talking about cameras, monitors, and photographs.
What is HDR: High Dynamic Range in photography
You'll see the term HDR used within the specifications of a lot of different products - cameras, televisions, microphones, and even industrial and medical equipment. In a general sense, HDR means that something has a wider range of acceptable inputs or outputs when compared to standard equipment. What we are going to focus on is the term HDR for camera and monitors.
HDR is about the amount of data the camera can capture at maximum exposure in a scene, from the darkest part to the lightest parts of the scene and is also known as HDR.
A common situation where you see the effects of dynamic range is when you take pictures in direct sunlight, you have enough light to work in such situations, but the differences in lighting are more noticeable, depending on the exposure of the camera, and the sky can be exaggerated, or it may Shadows appear under trees and other objects can appear Black.
If you are more interested in photography, you can check out the previous article in which we talked about the exposure triangle, you can find out What is the exposure triangle? And how to use it on smartphones.
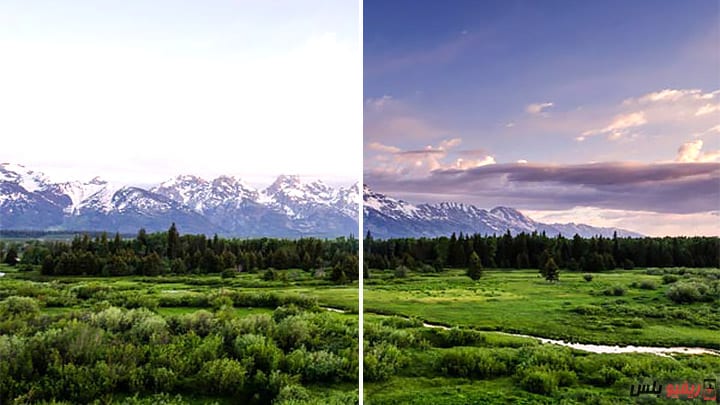
In the following example, you can see the difference between a photo taken without or with High Dynamic Range (HDR):-


This is a sample photo taken with a phone Samsung Galaxy S10 Shows High Dynamic Range.
How is HDR dynamic range measured?
Dynamic range or HDR is measured in stops, where each stop equals twice or half the amount of light, as increasing the exposure by one stop means double the light, if you shoot at a shutter speed of 1/100, then the exposure of one stop will be 1/50, Whereas it will be one stop darker than 1/200.
If you have a camera with one stop, this means that you can take a picture of a scene in which the lightest part is as bright as the darkest part, having a sensor with two stops of dynamic range will allow the lightest area of the scene to be four times brighter than the darkest point, bypassing this Borders will result in an image with distinct highlights or Black shadows.
We use smaller numbers to understand the term more easily, but most cameras have a large dynamic range, and a high-performance shooter like the Sony A7 III can have a dynamic range of 15 stops, but it's more common to see cameras with 12 to 14 stops, knowing that the eye Humanity has a dynamic range of 20 stops.
HDR screens
HDR images have nothing to do with HDR display technology. Both are used when the product is capable of doing something with a broader scope.
HDR screens do three things to make the image they display look better than a normal display, and we will review the three things with you in the following lines.
- HDR screens have a better contrast ratio that allows for brighter whites and darker Blacks at the same time, with both ends being sharp and well-defined.
- HDR provides a higher degree of color accuracy so that colors appear closer to what your eye would see if you were looking at things in real life (or seeing a product in real life).
- HDR also displays a wide color gamut (WCG) so more colors can be displayed on the same screen. A TV without WCG will not reproduce the actual color of the content displayed on it.
These three things are combined into one selling point called HDR. You might see other extras like 3D color management or a proprietary rendering engine like Dolby, but HDR itself needs to reproduce those basics. It really does look better if you see it next to the same content on a standard sized screen.
Content matters too. Your TV or phone can't create all of these new colors and put them where you think they should be. If you are watching standard videos, there will be no reduction in the image or video being displayed on the screen but when viewing HDR content on a non-HDR monitor, the color quality will be reduced to match the capabilities of the screen.
HDR content carries metadata along with the signal that tells the screen exactly how to display the content. The display itself just generates the appropriate color for each pixel according to the metadata and the image we see is brighter and more realistic.
When you want to play HDR content, you should pay close attention to the compatibility of all the components you have with HDR.
For example, you need an HDR-compatible Chromecast Ultra, a 4K HDR TV, a 4K HDR source, and enough bandwidth for the video stream and its associated metadata to get a good 4K HDR picture.
If one piece or component of that chain is broken, you'll get a standard high-resolution image without HDR.